Digital dentistry continues to move from innovation to everyday standard practice, driven by the need for greater efficiency, clinical precision, reduced treatment times, and an enhanced patient experience. By 2026, digital tools and artificial intelligence are no longer viewed as emerging technologies but as essential components of modern dentistry.
Key Trends and Technologies in Digital Dentistry
Intraoral Scanners (IOS)
Intraoral scanners are now central to efficient diagnosis and treatment planning, replacing traditional impression materials. Digital scans are more accurate and can be sent instantly to dental laboratories, eliminating postal delays and reducing the risk of impressions becoming distorted or damaged.
From a patient perspective, intraoral scanning is quicker, more comfortable, and significantly improves the overall clinical experience.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI is increasingly used to support early detection of dental issues, improve consistency in clinical decision-making, and enhance patient communication. Generative AI tools allow for advanced smile design, visualisation, and treatment planning, helping patients better understand proposed treatments.
AI is also supporting dental practices with non-clinical tasks such as appointment booking, workflow optimisation, and marketing.
Digital Workflows and CAD/CAM Technology
More practices and dental laboratories are transitioning to fully digital workflows, incorporating scanning, computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM), and 3D printing. These technologies are used to create crowns, bridges, dentures, and other restorations with greater precision and significantly faster turnaround times.
Teledentistry and Hybrid Care Models
Virtual consultations are becoming increasingly common for triage, treatment discussions, follow-ups, and orthodontic assessments. These hybrid models of care expand patient access, improve convenience, and help practices operate more efficiently.
Patient-Centred Digital Care
Digital tools allow dental professionals to personalise treatment plans using visual aids and simulations. This improves patient understanding, increases engagement, and supports informed decision-making, ultimately leading to better treatment acceptance and satisfaction.
Growth in Private Dentistry
Ongoing challenges with NHS dental provision, combined with rising patient expectations, are accelerating the shift towards private dentistry. As a result, practices are rapidly adopting advanced digital technologies and aesthetic procedures such as clear aligners, dental implants, and cosmetic bonding to meet demand.
Impact on Dental Practices and Professionals
Increased Efficiency and Accuracy
Digital dentistry reduces remakes caused by inaccurate or damaged impressions, optimises chair time, and improves collaboration between clinicians and laboratories. This leads to more predictable outcomes and higher standards of care.
Workforce Evolution and Skills Development
The adoption of digital technology requires new skillsets and a strong commitment to continuous professional development. Dentists and dental teams must remain confident in using and integrating new technologies into everyday workflows.
Regulatory Considerations
The General Dental Council (GDC) has outlined a strategy for 2026–2028 focused on “right-touch regulation that fits the times.” This includes addressing the ethical and regulatory implications of emerging digital technologies and artificial intelligence in dentistry.
The Future of Digital Dentistry
By 2026, digital dentistry is expected to be driven by integrated, data-led systems that improve both clinical efficiency and patient experience. Professionals are encouraged to actively explore and adopt these technologies to remain competitive in an evolving landscape.
As digital dentistry and AI become embedded in routine clinical practice, clinicians must not only be confident using these tools but also integrating them seamlessly. The ability to invest in and adapt to advanced digital solutions is becoming a key differentiator for modern dental practices.
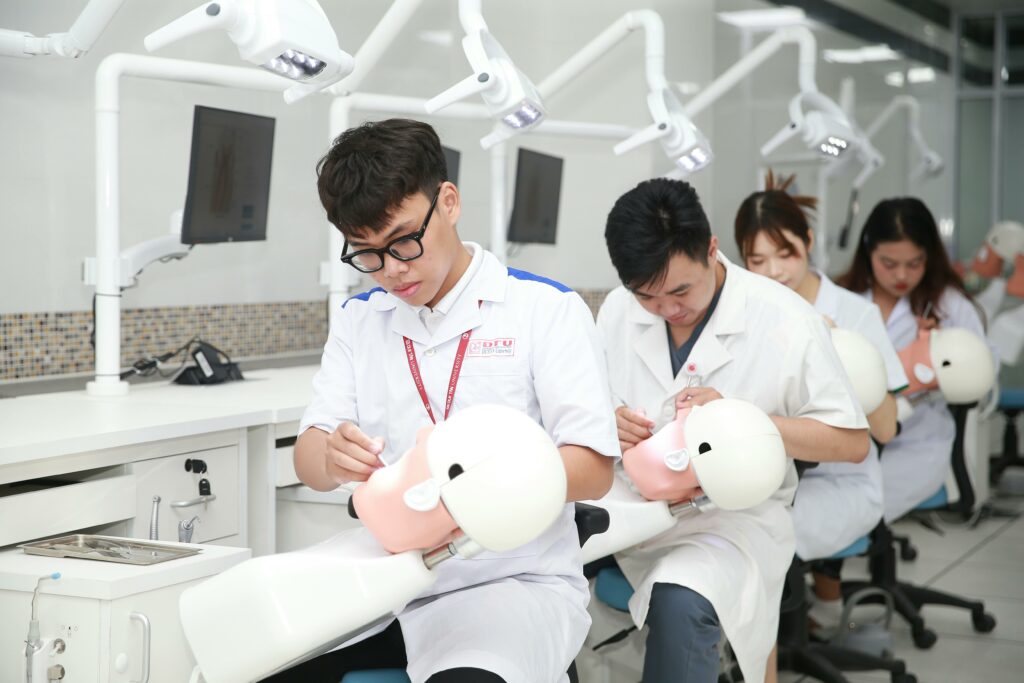
Digital Dentistry in Dental Education
Dental schools are playing a vital role in advancing digital dentistry by trialling and integrating chairside technologies into clinical education and patient care. These include augmented reality (AR) simulations, AI-powered diagnostic tools, and advanced digital workflows.
By using simulation technologies, students gain experience in a realistic, risk-free environment before treating patients.
King’s College London
The Faculty of Dentistry at King’s College London is a leader in digital dental education, using fully integrated digital workflows that include haptic dental workstations and SIMtoCARE simulators with augmented reality. Students can practise procedures such as drilling on virtual teeth while receiving real-time tactile feedback.
Real patient intraoral scans are converted into AR simulations for surgical practice, while CAD/CAM software and milling machines allow students to experience the full digital workflow from scan to manufacture.
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds has implemented virtual reality dental training, enabling students to practise on a wide range of complex cases that respond realistically to touch and technique.